Indications
- Moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) in adults.
- Relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS),
to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults.



ZEPOSIA Mechanism
Of Action (MOA)




ZEPOSIA Mechanism
Of Action (MOA)
ZEPOSIA Mechanism of Action (MOA)
ZEPOSIA: The Only Highly Selective S1P Receptor Modulator Specific to Receptors 1 and 5 in UC1,2
ZEPOSIA binds with a high affinity to S1P receptors 1 and 5 and has minimal or no activity on other S1P receptors (S1P2, S1P3, and S1P4)1
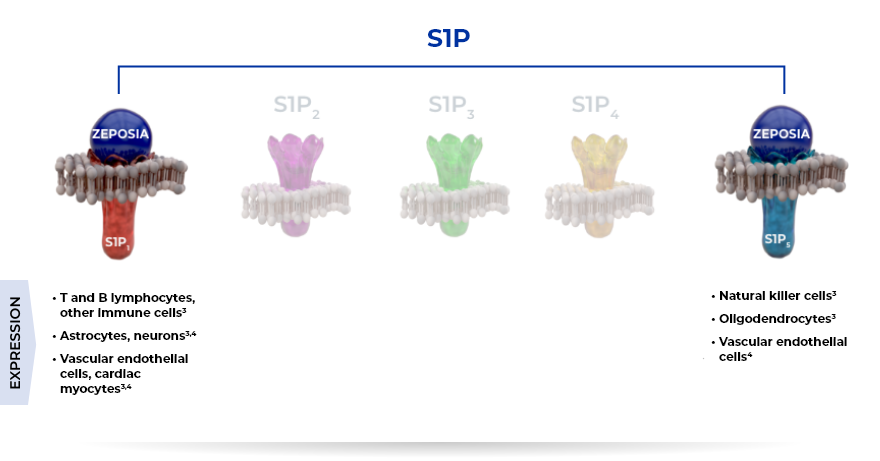
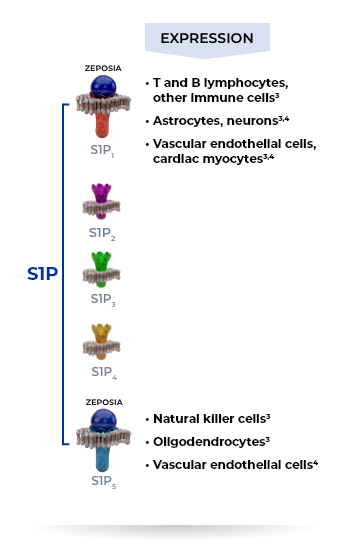
ZEPOSIA is an oral lymphocyte migration blocker that inhibits the capacity of inflammation-causing lymphocytes from reaching the inflamed colon1,5-10


Small molecules, like ZEPOSIA, may lack immunogenicity
and may not develop antidrug antibodies1,12,13
The mechanism by which ZEPOSIA exerts therapeutic effect is unknown, but may involve reduction of lymphocyte mitigation into the intestine.1
S1P=sphingosine 1-phosphate; UC=ulcerative colitis.

This website is best viewed
using the horizontal display on
your tablet device.

This website is best viewed
using the vertical display on
your mobile device.
- Patients who in the last 6 months, experienced myocardial infarction, unstable angina, stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), decompensated heart failure requiring hospitalization, or Class III/IV heart failure or have a presence of Mobitz type II second-degree or third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, sick sinus syndrome, or sino-atrial block, unless the patient has a functioning pacemaker
- Patients with severe untreated sleep apnea
- Patients taking a monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor
- Patients who in the last 6 months, experienced myocardial infarction, unstable angina, stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), decompensated heart failure requiring hospitalization, or Class III/IV heart failure or have a presence of Mobitz type II second-degree or third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, sick sinus syndrome, or sino-atrial block, unless the patient has a functioning pacemaker
- Patients with severe untreated sleep apnea
- Patients taking a monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor
- Herpes zoster and herpes simplex were seen in clinical trials of ZEPOSIA. Herpes simplex encephalitis and varicella zoster meningitis have been reported with sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulators. Patients without a healthcare professional-confirmed history of varicella (chickenpox), or without documentation of a full course of vaccination against varicella zoster virus (VZV), should be tested for antibodies to VZV before initiating ZEPOSIA.
- Cases of fatal cryptococcal meningitis (CM) and disseminated cryptococcal infections have been reported with S1P receptor modulators. If CM is suspected, ZEPOSIA should be suspended until cryptococcal infection has been excluded. If CM is diagnosed, appropriate treatment should be initiated.
- In the UC clinical studies, patients who received ZEPOSIA were not to receive concomitant treatment with antineoplastic, non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive, or immune-modulating therapies used for treatment of UC. Concomitant use of ZEPOSIA with any of these therapies would be expected to increase the risk of immunosuppression. When switching to ZEPOSIA from immunosuppressive medications, consider the duration of their effects and their mode of action to avoid unintended additive immunosuppressive effects.
- Use of live attenuated vaccines should be avoided during and for 3 months after treatment with ZEPOSIA. If live attenuated vaccine immunizations are required, administer at least 1 month prior to initiation of ZEPOSIA.
- with significant QT prolongation
- with arrhythmias requiring treatment with Class 1a or III anti-arrhythmic drugs
- with ischemic heart disease, heart failure, history of cardiac arrest or myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disease, and uncontrolled hypertension
- with a history of Mobitz type II second-degree or higher AV block, sick sinus syndrome, or sino-atrial heart block
References:
- Khan N, Abbas A, Williamson A, Balart L. Prevalence of corticosteroids use and disease course after initial steroid exposure in ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58(10):2963-2969.
- Burri E, Maillard MH, Schoepfer AM, et al. Treatment algorithm for mild and moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis: an update. Digestion. 2020;101(suppl 1):2-15.
- Lamb CA, Kennedy NA, Raine T, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology consensus guidelines on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut. 2019;68(suppl 3):s1-s106.
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Efficacy and safety study of ozanimod in ulcerative colitis (Touchstone). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01647516. Updated May 19, 2021. Accessed May 11, 2022.
References:
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, D’Haens G, et al; True North Study Group. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(14):1280-1291.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, D’Haens G, et al; True North Study Group. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis [supplementary appendix]. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(14):1280-1291.
- Danese S, Colombel JF, Ponich T, et al. Long-term use of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Oral Presentation at: ECCO 2022; February 16-19, 2022. Presentation DOP44.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0031. Princeton, NJ; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2022.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0022. Princeton, NJ; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2022.
- Wolf DC, Colombel JF, Ponich T, et al. Long-term use of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Poster presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW); San Diego, CA, and Virtual, May 21–24, 2022. Poster Tu1458.
- Long M, Cross R, Calkwood J, et al. Ozanimod first-dose cardiac effects in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis and relapsing multiple sclerosis. Poster presented at AIBD 2021; December 9–11, 2021.
References:
- Irving P, Long MD, Siegmund B, et al. Efficacy of ozanimod as an induction therapy in advanced therapy-naive ulcerative colitis patients suboptimally controlled on conventional treatments. Oral presentation at: United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; October 14–17, 2023. Presentation OP133.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, D’Haens G, et al; True North Study Group. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis [supplementary appendix]. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(14):1280-1291.
- Siegmund B, Axelrad J, Pondel M, et al. Rapidity of ozanimod-induced symptomatic response and remission in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: results from the induction period of True North. Oral presentation at: European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) Virtual; February 16–19, 2022.
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0066. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2023.
- Panaccione R, Afzali A, Hudesman D, et al. Extended therapy with ozanimod for delayed responders to ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: data from the True North open-label extension study. Poster presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW); San Diego, CA, and Virtual; May 21–24, 2022. Poster Tu1450.
- Siegmund B, Irving P, D’Haens G, et al. Ozanimod as a maintenance therapy in advanced therapy-naive ulcerative colitis patients with moderate vs severe endoscopic disease. Oral presentation at: United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; October 14–17, 2023. Presentation OP135.
- Danese S, Colombel JF, Ponich T, et al. Long-term use of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Oral presentation at: ECCO 2022: February 16–19, 2022. Presentation DOP44.
- Danese S, Abreu MT, Wolf DC, et al. Efficacy and safety of 3 years of continuous ozanimod treatment: an interim analysis of the True North open-label extension study. Oral presentation at: European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; March 1–4, 2023. Presentation DOP37.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Hanauer S, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: results from the open-label extension of the randomized, phase 2 TOUCHSTONE study.J Crohns Colitis. 2021;15(7):1120-1129.
- Panaccione R, Danese S, Wolf DC, et al. Long-term safety of 3 years of ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: an interim analysis of the True North open-label extension. Poster presented at: European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; March 1–4, 2023. Poster P405.
- Data on File. BMS_ZEP008535. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2022.
- Wolf DC, Colombel JF, Ponich T, et al. Long-term use of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Poster presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW); San Diego, CA, and Virtual; May 21–24, 2022. Poster Tu1458.
- Danese S, Panaccione R, Abreu MT, et al. Efficacy and safety of approximately 3 years of continuous ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: interim analysis of the True North open-label extension. J Crohns Colitis. Published online August 31, 2023. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjad146
References:
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Irving P, Long MD, Siegmund B, et al. Efficacy of ozanimod as an induction therapy in advanced therapy–naive ulcerative colitis patients suboptimally controlled on conventional treatments. Oral presentation at: United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; October 14–17, 2023. Presentation OP133.
References:
- Efficacy and safety study of ozanimod in ulcerative colitis (Touchstone). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01647516. Updated May 19, 2021. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Study of ozanimod (RPC1063) in relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS) (SUNBEAM). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02294058. Updated November 25, 2020. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- Efficacy and safety study of ozanimod in relapsing multiple sclerosis (RADIANCE). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02047734. Updated February 11, 2021. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- Efficacy and safety study of ozanimod (RPC1063) in relapsing multiple sclerosis patients (RADIANCE). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01628393. Updated November 2, 2021. Accessed September 6, 2023.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, D’Haens G, et al; True North Study Group. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(14):1280-1291.
- Safety and efficacy trial of RPC1063 for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis. ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02435992. Updated September 1, 2021. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- An extension study of RPC1063 as therapy for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis. ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02531126. Updated September 18, 2023. Accessed September 25, 2023.
- A multi-site, open-label extension trial of oral RPC1063 in relapsing multiple sclerosis. ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02576717. Updated January 30, 2024. Accessed February 6, 2024.
- Nakase H, Fujii T, Hisamatsu T, et al. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in Japan (J-True North). Poster presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2024; Washington, DC; May 18-21, 2024. Poster Su1795.
- Study describing cognitive processing speed changes in relapsing multiple sclerosis subjects treated with ozanimod (RPC-1063) (ENLIGHTEN). Clinicaltrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT0414035. Updated November 15, 2023. Accessed June 18, 2024.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0076. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0077. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Selmaj KW, Steinman L, Comi G, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of ozanimod in relapsing multiple sclerosis: final analysis of the DAYBREAK open-label extension study. Poster presented at: ACTRIMS 2024 Forum; February 29–March 2, 2024; West Palm Beach, FL. Poster P090.
- Press Release. U.S. Food and Drug Administration approves Bristol Myers Squibb’s ZEPOSIA® (ozanimod), a new oral treatment for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2020.
- Press Release. U.S. Food and Drug Administration approves Bristol Myers Squibb’s ZEPOSIA® (ozanimod), an oral treatment for adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2021.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-0079. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Siegel CA, Danese S, Rubin DT, et al. Safety of long-term ozanimod treatment for up to 4 years in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: an interim analysis of the True North open-label extension. Oral presentation at: European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) 2024; Stockholm, Sweden; February 21–24, 2024.
References:
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, D’Haens G, et al; True North Study Group. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(14):1280-1291.
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Panaccione R, Danese S, Wolf DC, et al. Long-term safety of 3 years of ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: an interim analysis of the True North open-label extension. Poster presented at: European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; March 1–4, 2023. Poster P405.
- Efficacy and safety study of ozanimod in ulcerative colitis (Touchstone). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01647516. Updated May 19, 2021. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- Long M, Cross RK, Lichtenstein GR, et al. Long-term cardiac safety of ozanimod in phase 3 clinical program of ulcerative colitis and relapsing multiple sclerosis. Presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW); San Diego, CA, and Virtual; May 21–24, 2022. Presentation 15.
- Rieder F, Wolf DC, Charles L, Kollengode K, Patel A, Ghosh S. Incidence of infections in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis treated with ozanimod and relationship to significant lymphopenia: results from a pooled safety analysis. Poster presented at: DDW 2021 Virtual Digestive Disease Week; May 21–23, 2021.
- Danese S, Feagan BG, Wolf DC. Ozanimod as maintenance therapy in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis: results from the phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled True North study. Paper presented at: United European Gastroenterology Week Virtual 2020; October 10–14, 2020. Presentation LB10.
- D’Haens G, Colombel JF, Lichtenstein GR, et al. Safety of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis over time: pooled analysis from phase 2, phase 3, and open-label extension trials. Oral presentation at: DDW 2021 Virtual Digestive Disease Week; May 21–23, 2021.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Hanauer S, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: results from the open-label extension of the randomized, phase 2 TOUCHSTONE study. J Crohns Colitis. 2021;15(7):1120-1129.
- Siegel CA, Danese S, Rubin DT, et al. Safety of long-term ozanimod treatment for up to 4 years in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: an interim analysis of the True North open-label extension. Oral presentation at: European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) 2024; Stockholm, Sweden; February 21–24, 2024.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0066. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2022.
- Wolf DC, Colombel JF, Ponich T, et al. Long-term use of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Poster presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW); San Diego, CA, and Virtual; May 21–24, 2022. Poster Tu1458.
References:
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Sandborn WJ, Vermeire S, Peyrin-Biroulet L, et al. Etrasimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis (ELEVATE): two randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies [published correction appears in Lancet. 2023 Mar 25;401(10381):1000]. Lancet. 2023;401(10383):1159-1171.
- McGinley MP, Cohen JA. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulators in multiple sclerosis and other conditions [published correction appears in Lancet. 2021 Sep 25;398(10306):1132]. Lancet. 2021;398(10306):1184-1194.
- Roggeri A, Schepers M, Tiane A, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulators and oligodendroglial cells: beyond immunomodulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7537.
- Pérez-Jeldres T, Tyler CJ, Boyer JD, et al. Cell trafficking interference in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019;2(25):270-282.
- Al-Bawardy B, Shivashankar R, Proctor DD. Novel and emerging therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:651415.
- Nikolakis D, de Voogd FAE, Pruijit MJ, et al. The role of the lymphatic system in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1854.
- Harris S, Tran JQ, Southworth H, Spencer CM, Cree BAC, Zamvil SS. Effect of the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator ozanimod on leukocyte subtypes in relapsing MS. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2020;7(5):e839.
- Jaigirdar SA, Benson RA, Elmesmari A, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate promotes the persistence of activated CD4 T cells in inflamed sites. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1627.
- Scott FL, Clemons B, Brooks J, et al. Ozanimod (RPC1063) is a potent sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 (S1P1) and receptor-5 (S1P5) agonist with autoimmune disease-modifying activity. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173:1778-1792.
- Kayal M, Shah S. Ulcerative colitis: current and emerging treatment strategies. J Clin Med. 2019;9(1):94.
- Olivera P, Danese S, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Next generation of small molecules in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 2017;66(2):199-209.
- Lucaciu LA, Seicean R, Seicean A. Small molecule drugs in the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases: which one, when and why? – a systematic review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;32(6):669-677.
Reference:
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.

