Indications
- Moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) in adults.
- Relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS),
to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults.




ZEPOSIA Demonstrated
Safety Profile1




ZEPOSIA Demonstrated
Safety Profile1
ZEPOSIA Offers Patients a Demonstrated Safety Profile

Low discontinuation rates
due to treatment-emergent adverse events that are comparable to placebo1a


Rates of serious infection were low and comparable to placebo in clinical trials2bc


Demonstrated safety profile
and long-term safety data observed for over 4 years1-3

aOverall rates of discontinuation were 6.5% with ZEPOSIA (N=429) vs 11.1% with placebo (N=216) in the induction phase, and 20% with ZEPOSIA (N=230) vs 45.4% with placebo (N=227) in the maintenance phase. Discontinuation rates due to TEAEs in induction were 3.3% for patients taking ZEPOSIA vs 3.2% for patients taking placebo. In maintenance, TEAE discontinuation rates were 1.3% for patients taking ZEPOSIA vs 2.6% for patients taking placebo.1,2
bOverall rates of infection were 9.9% with ZEPOSIA (N=496) vs 10.7% with placebo (N=281) in the induction phase, and 23% with ZEPOSIA (N=230) vs 12% with placebo (N=227) in the maintenance phase. Serious infection rates in the induction phase (UC Study 1 and UC Study 3/TOUCHSTONE) were 0.8% with ZEPOSIA vs 0.4% with placebo. Serious infection rates in the maintenance phase were 0.9% with ZEPOSIA vs 1.8% with placebo.2
cAdditional data from the induction period of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (UC Study 3/TOUCHSTONE) included 67 patients who received ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg once daily.2
|
Adverse Reaction
|
ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg (n=496)gh |
Placebo (n=281)g |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Respiratory Infectione | 5% | 4% |
| Liver Test Increasedf | 5% | 0% |
| Headache | 4% | 3% |
| Pyrexia | 3% | 2% |
| Nausea | 3% | 2% |
| Arthralgia | 3% | 1% |
(UC Study 2)
|
Adverse Reaction
|
ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg (n=230) |
Placebo (n=227) |
|---|---|---|
| Liver Test Increasedi | 11% | 2% |
| Headache | 5% | <1% |
- dAdditional data from the induction period of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (UC Study 3/TOUCHSTONE) included 67 patients who received ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg once daily.2
- eIncludes the following terms: streptococcal pharyngitis, pharyngotonsillitis, bacterial pharyngitis, nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, viral upper respiratory tract infection, laryngitis, acute sinusitis, catarrh, chronic sinusitis, upper respiratory tract inflammation, chronic tonsillitis, viral pharyngitis, viral sinusitis, bacterial sinusitis, bacterial upper respiratory tract infection, viral labyrinthitis, laryngeal inflammation, and pharyngeal inflammation.2
- fIncludes the following terms: gamma-glutamyl transferase increased, alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, hepatic enzyme increased, hyperbilirubinemia, liver function test increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, and transaminases increased.2
- gPercentages were calculated as the sum of each individual study percentage multiplied by its Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel weight.2
- hZEPOSIA was initiated with a 7-day titration.2
- iIncludes the following terms: gamma-glutamyl transferase increased, alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, hepatic enzyme increased, hyperbilirubinemia, liver function test increased, and blood alkaline phosphatase increased.2
UC Study 3 (8-week induction): TOUCHSTONE is a phase 2, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo- controlled parallel-group study to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of induction therapy with ZEPOSIA in 199 patients with moderately to severely active UC. Participants who completed the induction period and were responders at Week 8 continued to receive the same dose of ZEPOSIA during the maintenance period up to Week 32.4
For full study design of UC Study 1 and Study 2, click here.
(n=429)
(n=216)
| Adverse Event | 40.1% | 38% |
| Serious Adverse Event |
4% | 3.2% |
(n=230)
(n=227)
| Adverse Event | 49.1% | 36.6% |
| Serious Adverse Event |
5.2% | 7.9% |
- jIn the TRUE NORTH phase 3 studies, 1 case of ischemic stroke (0.2%) was reported in ZEPOSIA-treated patients vs no reports in patients treated with placebo.5
- kThromboembolic events include pulmonary embolism and venous arterial thrombosis. Major or adverse cardiac events include cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and stroke.5
TEAE=treatment-emergent adverse event; UC=ulcerative colitis.
| ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg (n=429) |
Placebo (n=216) |
ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg (n=230) |
Placebo (n=227) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
ALT ≥3x ULN |
2.6% | 0.5% | 2.3% | 0% |
ALT ≥5x ULN |
0.9% | 0.5% | 0.9% | 0% |
- In controlled and uncontrolled UC studies, the majority (96%) of patients with ALT >3X ULN continued treatment with ZEPOSIA, with values returning to <3X ULN within ~2-4 weeks2
- The overall discontinuation rate because of elevations in hepatic enzymes was 0.4% in patients treated with ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg and none in patients who received placebo in the controlled UC studies2
- Patients who develop symptoms suggestive of hepatic dysfunction, such as unexplained nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, anorexia, or jaundice and/or dark urine, should have hepatic enzymes checked, and ZEPOSIA should be discontinued if significant liver injury is confirmed2
ALT=alanine aminotransferase; LFT=liver function test; UC=ulcerative colitis; ULN=upper limit of normal.
In controlled clinical trials with ZEPOSIA, mean lymphocyte counts decreased to approximately 45% of baseline at 3 months (approximate mean blood lymphocyte counts 0.8 x 109/L), and low lymphocyte counts were maintained during treatment with ZEPOSIA.2
- The proportion of patients treated with ZEPOSIA with lymphocytes less than 0.2 x 109/L was 2.0% in UC Study 1 and Study 3 (phase 2) and 2.3% in UC Study 22
- These values generally returned to greater than 0.2 x 109/L while patients remained on treatment with ZEPOSIA2
- After discontinuing treatment, the median time for peripheral blood lymphocytes to return to the normal range was approximately 30 days2
- Approximately 80% to 90% of patients were in the normal range within 3 months2
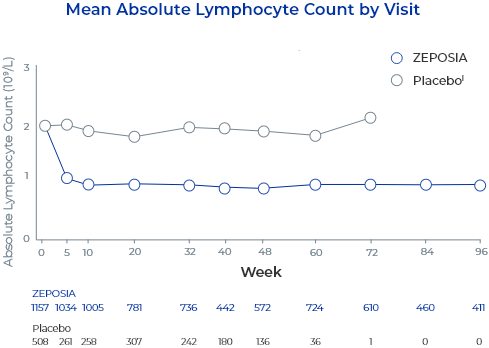
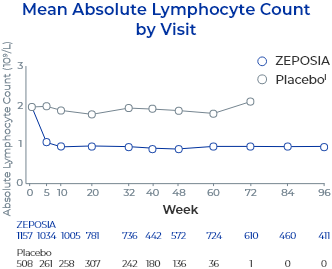
- Descriptive pooled analysis of controlled and uncontrolled trials including the 32-week phase 2 TOUCHSTONE trial, the 52-week phase 3 TRUE NORTH trial, and an open-label extension study. Patients completing ≥1 year of the TOUCHSTONE OLE could roll over into the TRUE NORTH OLE6
- Reductions in ALC were observed at Week 5 (the first post-baseline assessment) and sustained through treatment6
- 60 patients (5.3%) had ALC <0.2 x 109/L at least once during ZEPOSIA treatment6
- Most patients (98.3%; n=59) returned to ALC ≥0.2 x 109/L at the time of the analysis; 89.8% returned to ≥0.2 x 109/L while continuing treatment with ZEPOSIA6
- lPatients may be included in both placebo and ZEPOSIA treatment groups. The total count in the placebo group includes 227 patients who were treated with ZEPOSIA in the induction period and were re-randomized to placebo in the maintenance period of TRUE NORTH.6
OLE=open-label extension; UC=ulcerative colitis.
Low Discontinuation Rates
Discontinuation Rates Due
to TEAEs That Are Comparable
to Placebo1
UC Study 1—Induction:
6.5% for ZEPOSIA | 11.1% for Placebo
UC Study 2—Maintenance:
20.0% for ZEPOSIA | 45.4% for Placebo
to Treatment-Emergent
Adverse Events (TEAEs)1
Induction
3.3%
ZEPOSIA
vs 3.2%
for placebo
Maintenance
1.3%
ZEPOSIA
vs 2.6%
for placebo
One case of macular edema was reported during the maintenance phase in 1 person with preexisting risk factors at baseline; it resolved after discontinuation of treatment.1,7
Overall, the discontinuation rate because of elevations in hepatic enzymes was 0.4% in patients treated with ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg and none in patients who received placebo in the controlled UC studies.2
TEAEs=treatment-emergent adverse events; UC=ulcerative colitis.
Infections and Malignancies
Rates of Serious Infection Were Low and Comparable to Placebo in Clinical Trials2
Clinical Trials2
Infection |
ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg (n=496) |
Placebo (n=281) |
ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg (n=230) |
Placebo (n=227) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Overall Rate of Infection |
9.9% | 10.7% | 23% | 12% |
Serious Infections |
0.8% | 0.4% | 0.9% | 1.8% |
Herpes Zoster |
0.4% | 0% | 2.2% | 0.4% |
- Malignancies, such as melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, breast cancer, seminoma, cervical carcinoma, and adenocarcinomas, including rectal adenocarcinoma, were reported with ZEPOSIA in controlled trials of multiple sclerosis and UC. An increased risk of cutaneous malignancies has been reported with another S1P receptor modulator2
- mAdditional data from the induction period of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (UC Study 3/TOUCHSTONE) included 67 patients who received ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg once daily.2
| Malignancies Malig- nancies |
ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg (n=429) |
Placebo (n=216) |
ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg (n=230) |
Placebo (n=227) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Basal Cell Carcinoma |
0% | 0% | 0.4% | 0% |
Rectal Adenocar- cinoma |
0% | 0% | 0.4% | 0% |
Adenocar- cinoma of the Colon |
0% | 0% | 0% | 0.4% |
Breast Cancer |
0% | 0% | 0% | 0.4% |
(n=1158)
PY=1922.5n
(n=508)
PY=249.2n
| % (n) | IR, per 100 PYo | % (n) | IR, per 100 PYo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Any Infection |
29.1 (337) | 22.81 | 14.0 (71) | 31.43 |
Any Serious Infection |
2.2 (25) | 1.32 | 1.4 (7) | 2.84 |
Malignan- cies |
1.0 (12) | 0.63 | 0.4 (2) | 0.81 |
- Safety outcomes were analyzed using descriptive statistics on pooled data from all controlled and uncontrolled UC trials: participants from 32-week TOUCHSTONE trialp (phase 2), 52-week TRUE NORTH trial (phase 3), and the respective OLE trials8
- Median treatment duration in weeks for ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg and placebo was 65.79 and 17.21, respectively8
- TEAEs identified in the pooled data from all controlled and uncontrolled UC trials were consistent with the controlled UC trials8
- nTotal PY equals the sum of the number of years on study contributed by each patient from time of first dose per treatment group in the pool to last date on study per treatment group in the pool. The algorithm for the last date on study is dependent on patient disposition and whether the patient enrolled into an extension study.8
- oIncidence rate per 100 PY, calculated as number of patients/PY x 100 for specific SOC category or PT subcategory. Analysis was based on the treatment group to which a patient was assigned when the event occurred, including patients who were
re-randomized to placebo.8 - pTOUCHSTONE patients randomized to ZEPOSIA 0.46 mg unapproved dose were only analyzed upon entering TOUCHSTONE OLE and receiving daily ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg.9
IR=incidence rate; OLE=open-label extension; PT=preferred term; PY=patient-years; S1P=sphingosine 1-phosphate; SOC=system organ class; TEAE=treatment-emergent adverse event; UC=ulcerative colitis.
Long-Term Safety Data Observed Over ~4 Years With ZEPOSIA3,10
This Safety Analysis Includes Patients With UC From the TRUE NORTH Parent Study Who Entered the TRUE NORTH OLE for up to 194 Weeks of ZEPOSIA Exposure10
Estimated Annual Risk = 2.5 per 100 treated patients10

TEAEs Leading
to
Treatment Discontinuation10
2.5
EAIR per
100 PYq
Serious TEAEs10
7.0
EAIR per
100 PYq
Serious Infection10
1.8
EAIR per
100 PYq
in OLE
(N=823)
| EAIR per 100 PYq | |
|---|---|
| TEAEs | 85.5 |
| Serious TEAEs | 7.0 |
| TEAEs Leading to Treatment Discontinuation |
2.5 |
| Most Frequent TEAEs (Occurring in ≥8% of Patients) | |
| Lymphopeniar | 6.1 |
| COVID-19 | 4.3 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 3.8 |
| Anemiar | 3.7 |
| Lymphocyte Count Decreasedr | 3.7 |
| Alanine Aminotransferase Increasedr | 3.2 |
| Arthralgia | 3.2 |
| Headache | 2.8 |
| Infection (Occurring in ≥3.0% of Patients) | |
| COVID-19 | 4.3 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 3.8 |
| Upper Respiratory Tract Infection | 2.4 |
| Serious Infection | 1.8 |
| Herpes Zoster | 1.2 |
| Sinusitis | 1.2 |
| Bronchitis11 | 1.1 |
| Influenza11 | 1.0 |
| Malignancy (Serious TEAE)11 | |
| Basal Cell Carcinoma | 0.04 |
| Colon Adenocarcinoma | 0.04 |
| Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | 0.04 |
| B-Cell Lymphoma | 0.04 |
| Follicular Lymphoma, Stage IV | 0.04 |
| Malignant Lung Neoplasm | 0.04 |
| Prostate Cancer | 0.04 |
| Rectal Adenocarcinoma | 0.04 |
| Rectal Cancer Stage II | 0.04 |
| Cardiovascular Disorders | |
| Hypertension | 2.3 |
| Hypertensive Crisis | 0.16 |
| Bradycardia | 0.12 |
| Myocardial Ischemia | 0.12 |
| Ischemic Stroke | 0.12 |
| Pulmonary Embolism | 0.12 |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis | 0.12 |
| Third-Degree AV Block | 0.04 |
| Macular Edema | 0.2 |
Three deaths were reported during the OLE: 1 sudden death, 1 due to COVID-19, and 1 due to adenocarcinoma. These deaths were deemed to be unrelated to ZEPOSIA treatment by investigators.3,10
Infection (Occurring in ≥3.5% of Patients)10
COVID-19:
4.3 EAIR per 100 PYq
Nasopharyngitis:
3.8 EAIR per 100 PYq
Upper Respiratory Tract Infection:
2.4 EAIR per 100 PYq
- qEAIRs were calculated as numbers of patients/PY × 100.10
- rLaboratory values were flagged by the central laboratory if they fell outside the standard reference range; investigators decided whether laboratory values qualified as adverse events.12
AV=atrioventricular; EAIR=exposure-adjusted incidence rate; OLE=open-label extension; PY=patient-years; TEAE=treatment-emergent adverse event; UC=ulcerative colitis.

This website is best viewed
using the horizontal display on
your tablet device.

This website is best viewed
using the vertical display on
your mobile device.
- Patients who in the last 6 months, experienced myocardial infarction, unstable angina, stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), decompensated heart failure requiring hospitalization, or Class III/IV heart failure or have a presence of Mobitz type II second-degree or third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, sick sinus syndrome, or sino-atrial block, unless the patient has a functioning pacemaker
- Patients with severe untreated sleep apnea
- Patients taking a monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor
- Patients who in the last 6 months, experienced myocardial infarction, unstable angina, stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), decompensated heart failure requiring hospitalization, or Class III/IV heart failure or have a presence of Mobitz type II second-degree or third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, sick sinus syndrome, or sino-atrial block, unless the patient has a functioning pacemaker
- Patients with severe untreated sleep apnea
- Patients taking a monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor
- Herpes zoster and herpes simplex were seen in clinical trials of ZEPOSIA. Herpes simplex encephalitis and varicella zoster meningitis have been reported with sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulators. Patients without a healthcare professional-confirmed history of varicella (chickenpox), or without documentation of a full course of vaccination against varicella zoster virus (VZV), should be tested for antibodies to VZV before initiating ZEPOSIA.
- Cases of fatal cryptococcal meningitis (CM) and disseminated cryptococcal infections have been reported with S1P receptor modulators. If CM is suspected, ZEPOSIA should be suspended until cryptococcal infection has been excluded. If CM is diagnosed, appropriate treatment should be initiated.
- In the UC clinical studies, patients who received ZEPOSIA were not to receive concomitant treatment with antineoplastic, non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive, or immune-modulating therapies used for treatment of UC. Concomitant use of ZEPOSIA with any of these therapies would be expected to increase the risk of immunosuppression. When switching to ZEPOSIA from immunosuppressive medications, consider the duration of their effects and their mode of action to avoid unintended additive immunosuppressive effects.
- Use of live attenuated vaccines should be avoided during and for 3 months after treatment with ZEPOSIA. If live attenuated vaccine immunizations are required, administer at least 1 month prior to initiation of ZEPOSIA.
- with significant QT prolongation
- with arrhythmias requiring treatment with Class 1a or III anti-arrhythmic drugs
- with ischemic heart disease, heart failure, history of cardiac arrest or myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disease, and uncontrolled hypertension
- with a history of Mobitz type II second-degree or higher AV block, sick sinus syndrome, or sino-atrial heart block
References:
- Khan N, Abbas A, Williamson A, Balart L. Prevalence of corticosteroids use and disease course after initial steroid exposure in ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58(10):2963-2969.
- Burri E, Maillard MH, Schoepfer AM, et al. Treatment algorithm for mild and moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis: an update. Digestion. 2020;101(suppl 1):2-15.
- Lamb CA, Kennedy NA, Raine T, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology consensus guidelines on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut. 2019;68(suppl 3):s1-s106.
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Efficacy and safety study of ozanimod in ulcerative colitis (Touchstone). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01647516. Updated May 19, 2021. Accessed May 11, 2022.
References:
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, D’Haens G, et al; True North Study Group. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(14):1280-1291.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, D’Haens G, et al; True North Study Group. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis [supplementary appendix]. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(14):1280-1291.
- Danese S, Colombel JF, Ponich T, et al. Long-term use of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Oral Presentation at: ECCO 2022; February 16-19, 2022. Presentation DOP44.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0031. Princeton, NJ; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2022.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0022. Princeton, NJ; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2022.
- Wolf DC, Colombel JF, Ponich T, et al. Long-term use of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Poster presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW); San Diego, CA, and Virtual, May 21–24, 2022. Poster Tu1458.
- Long M, Cross R, Calkwood J, et al. Ozanimod first-dose cardiac effects in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis and relapsing multiple sclerosis. Poster presented at AIBD 2021; December 9–11, 2021.
References:
- Irving P, Long MD, Siegmund B, et al. Efficacy of ozanimod as an induction therapy in advanced therapy-naive ulcerative colitis patients suboptimally controlled on conventional treatments. Oral presentation at: United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; October 14–17, 2023. Presentation OP133.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, D’Haens G, et al; True North Study Group. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis [supplementary appendix]. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(14):1280-1291.
- Siegmund B, Axelrad J, Pondel M, et al. Rapidity of ozanimod-induced symptomatic response and remission in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: results from the induction period of True North. Oral presentation at: European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) Virtual; February 16–19, 2022.
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0066. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2023.
- Panaccione R, Afzali A, Hudesman D, et al. Extended therapy with ozanimod for delayed responders to ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: data from the True North open-label extension study. Poster presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW); San Diego, CA, and Virtual; May 21–24, 2022. Poster Tu1450.
- Siegmund B, Irving P, D’Haens G, et al. Ozanimod as a maintenance therapy in advanced therapy-naive ulcerative colitis patients with moderate vs severe endoscopic disease. Oral presentation at: United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; October 14–17, 2023. Presentation OP135.
- Danese S, Colombel JF, Ponich T, et al. Long-term use of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Oral presentation at: ECCO 2022: February 16–19, 2022. Presentation DOP44.
- Danese S, Abreu MT, Wolf DC, et al. Efficacy and safety of 3 years of continuous ozanimod treatment: an interim analysis of the True North open-label extension study. Oral presentation at: European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; March 1–4, 2023. Presentation DOP37.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Hanauer S, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: results from the open-label extension of the randomized, phase 2 TOUCHSTONE study.J Crohns Colitis. 2021;15(7):1120-1129.
- Panaccione R, Danese S, Wolf DC, et al. Long-term safety of 3 years of ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: an interim analysis of the True North open-label extension. Poster presented at: European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; March 1–4, 2023. Poster P405.
- Data on File. BMS_ZEP008535. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2022.
- Wolf DC, Colombel JF, Ponich T, et al. Long-term use of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Poster presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW); San Diego, CA, and Virtual; May 21–24, 2022. Poster Tu1458.
- Danese S, Panaccione R, Abreu MT, et al. Efficacy and safety of approximately 3 years of continuous ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: interim analysis of the True North open-label extension. J Crohns Colitis. Published online August 31, 2023. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjad146
References:
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Irving P, Long MD, Siegmund B, et al. Efficacy of ozanimod as an induction therapy in advanced therapy–naive ulcerative colitis patients suboptimally controlled on conventional treatments. Oral presentation at: United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; October 14–17, 2023. Presentation OP133.
References:
- Efficacy and safety study of ozanimod in ulcerative colitis (Touchstone). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01647516. Updated May 19, 2021. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Study of ozanimod (RPC1063) in relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS) (SUNBEAM). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02294058. Updated November 25, 2020. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- Efficacy and safety study of ozanimod in relapsing multiple sclerosis (RADIANCE). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02047734. Updated February 11, 2021. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- Efficacy and safety study of ozanimod (RPC1063) in relapsing multiple sclerosis patients (RADIANCE). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01628393. Updated November 2, 2021. Accessed September 6, 2023.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, D’Haens G, et al; True North Study Group. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(14):1280-1291.
- Safety and efficacy trial of RPC1063 for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis. ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02435992. Updated September 1, 2021. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- An extension study of RPC1063 as therapy for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis. ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02531126. Updated September 18, 2023. Accessed September 25, 2023.
- A multi-site, open-label extension trial of oral RPC1063 in relapsing multiple sclerosis. ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02576717. Updated January 30, 2024. Accessed February 6, 2024.
- Nakase H, Fujii T, Hisamatsu T, et al. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in Japan (J-True North). Poster presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2024; Washington, DC; May 18-21, 2024. Poster Su1795.
- Study describing cognitive processing speed changes in relapsing multiple sclerosis subjects treated with ozanimod (RPC-1063) (ENLIGHTEN). Clinicaltrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT0414035. Updated November 15, 2023. Accessed June 18, 2024.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0076. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0077. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Selmaj KW, Steinman L, Comi G, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of ozanimod in relapsing multiple sclerosis: final analysis of the DAYBREAK open-label extension study. Poster presented at: ACTRIMS 2024 Forum; February 29–March 2, 2024; West Palm Beach, FL. Poster P090.
- Press Release. U.S. Food and Drug Administration approves Bristol Myers Squibb’s ZEPOSIA® (ozanimod), a new oral treatment for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2020.
- Press Release. U.S. Food and Drug Administration approves Bristol Myers Squibb’s ZEPOSIA® (ozanimod), an oral treatment for adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2021.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-0079. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Siegel CA, Danese S, Rubin DT, et al. Safety of long-term ozanimod treatment for up to 4 years in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: an interim analysis of the True North open-label extension. Oral presentation at: European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) 2024; Stockholm, Sweden; February 21–24, 2024.
References:
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, D’Haens G, et al; True North Study Group. Ozanimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(14):1280-1291.
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Panaccione R, Danese S, Wolf DC, et al. Long-term safety of 3 years of ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: an interim analysis of the True North open-label extension. Poster presented at: European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) 2023; Copenhagen, Denmark; March 1–4, 2023. Poster P405.
- Efficacy and safety study of ozanimod in ulcerative colitis (Touchstone). ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01647516. Updated May 19, 2021. Accessed July 26, 2023.
- Long M, Cross RK, Lichtenstein GR, et al. Long-term cardiac safety of ozanimod in phase 3 clinical program of ulcerative colitis and relapsing multiple sclerosis. Presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW); San Diego, CA, and Virtual; May 21–24, 2022. Presentation 15.
- Rieder F, Wolf DC, Charles L, Kollengode K, Patel A, Ghosh S. Incidence of infections in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis treated with ozanimod and relationship to significant lymphopenia: results from a pooled safety analysis. Poster presented at: DDW 2021 Virtual Digestive Disease Week; May 21–23, 2021.
- Danese S, Feagan BG, Wolf DC. Ozanimod as maintenance therapy in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis: results from the phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled True North study. Paper presented at: United European Gastroenterology Week Virtual 2020; October 10–14, 2020. Presentation LB10.
- D’Haens G, Colombel JF, Lichtenstein GR, et al. Safety of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis over time: pooled analysis from phase 2, phase 3, and open-label extension trials. Oral presentation at: DDW 2021 Virtual Digestive Disease Week; May 21–23, 2021.
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Hanauer S, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of ozanimod in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: results from the open-label extension of the randomized, phase 2 TOUCHSTONE study. J Crohns Colitis. 2021;15(7):1120-1129.
- Siegel CA, Danese S, Rubin DT, et al. Safety of long-term ozanimod treatment for up to 4 years in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: an interim analysis of the True North open-label extension. Oral presentation at: European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) 2024; Stockholm, Sweden; February 21–24, 2024.
- Data on File. BMS-REF-OZA-0066. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2022.
- Wolf DC, Colombel JF, Ponich T, et al. Long-term use of ozanimod in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. Poster presented at: Digestive Disease Week (DDW); San Diego, CA, and Virtual; May 21–24, 2022. Poster Tu1458.
References:
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Sandborn WJ, Vermeire S, Peyrin-Biroulet L, et al. Etrasimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis (ELEVATE): two randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies [published correction appears in Lancet. 2023 Mar 25;401(10381):1000]. Lancet. 2023;401(10383):1159-1171.
- McGinley MP, Cohen JA. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulators in multiple sclerosis and other conditions [published correction appears in Lancet. 2021 Sep 25;398(10306):1132]. Lancet. 2021;398(10306):1184-1194.
- Roggeri A, Schepers M, Tiane A, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulators and oligodendroglial cells: beyond immunomodulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7537.
- Pérez-Jeldres T, Tyler CJ, Boyer JD, et al. Cell trafficking interference in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019;2(25):270-282.
- Al-Bawardy B, Shivashankar R, Proctor DD. Novel and emerging therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:651415.
- Nikolakis D, de Voogd FAE, Pruijit MJ, et al. The role of the lymphatic system in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1854.
- Harris S, Tran JQ, Southworth H, Spencer CM, Cree BAC, Zamvil SS. Effect of the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator ozanimod on leukocyte subtypes in relapsing MS. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2020;7(5):e839.
- Jaigirdar SA, Benson RA, Elmesmari A, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate promotes the persistence of activated CD4 T cells in inflamed sites. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1627.
- Scott FL, Clemons B, Brooks J, et al. Ozanimod (RPC1063) is a potent sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-1 (S1P1) and receptor-5 (S1P5) agonist with autoimmune disease-modifying activity. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173:1778-1792.
- Kayal M, Shah S. Ulcerative colitis: current and emerging treatment strategies. J Clin Med. 2019;9(1):94.
- Olivera P, Danese S, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Next generation of small molecules in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 2017;66(2):199-209.
- Lucaciu LA, Seicean R, Seicean A. Small molecule drugs in the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases: which one, when and why? – a systematic review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;32(6):669-677.
Reference:
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.