Contraindications:
- Patients who in the last 6 months, experienced myocardial infarction, unstable angina, stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), decompensated heart failure requiring hospitalization, or Class III/IV heart failure or have a presence of Mobitz type II second-degree or third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, sick sinus syndrome, or sino-atrial block, unless the patient has a functioning pacemaker
- Patients with severe untreated sleep apnea
- Patients taking a monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor
Infections: ZEPOSIA may increase the susceptibility to infections. Life-threatening and rare fatal infections have occurred in patients receiving ZEPOSIA. Obtain a recent (i.e., within 6 months or after discontinuation of prior MS or UC therapy) complete blood count (CBC) including lymphocyte count before initiation of ZEPOSIA. Delay initiation of ZEPOSIA in patients with an active infection until the infection is resolved. Consider interruption of treatment with ZEPOSIA if a patient develops a serious infection. Continue monitoring for infections up to 3 months after discontinuing ZEPOSIA.
- Herpes zoster and herpes simplex were seen in clinical trials of ZEPOSIA. Herpes simplex encephalitis and varicella zoster meningitis have been reported with sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulators. Patients without a healthcare professional-confirmed history of varicella (chickenpox), or without documentation of a full course of vaccination against varicella zoster virus (VZV), should be tested for antibodies to VZV before initiating ZEPOSIA.
- Cases of fatal cryptococcal meningitis (CM) and disseminated cryptococcal infections have been reported with S1P receptor modulators. If CM is suspected, ZEPOSIA should be suspended until cryptococcal infection has been excluded. If CM is diagnosed, appropriate treatment should be initiated.
- In the MS and UC clinical studies, patients who received ZEPOSIA were not to receive concomitant treatment with antineoplastic, non-corticosteroid immunosuppressive, or immune-modulating therapies used for treatment of MS and UC. Concomitant use of ZEPOSIA with any of these therapies would be expected to increase the risk of immunosuppression. When switching to ZEPOSIA from immunosuppressive medications, consider the duration of their effects and their mode of action to avoid unintended additive immunosuppressive effects.
- Use of live attenuated vaccines should be avoided during and for 3 months after treatment with ZEPOSIA. If live attenuated vaccine immunizations are required, administer at least 1 month prior to initiation of ZEPOSIA.
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML): PML is an opportunistic viral infection of the brain that typically occurs in patients who are immunocompromised, and that usually leads to death or severe disability.
PML has been reported in patients treated with S1P receptor modulators, including ZEPOSIA, and other MS and UC therapies and has been associated with some risk factors (e.g., immunocompromised patients, polytherapy with immunosuppressants, duration of use). Based on data from patients with MS, longer treatment duration increases the risk of PML in patients treated with S1P receptor modulators, and the majority of PML cases have occurred in patients treated with S1P receptor modulators for at least 18 months. If PML is suspected, withhold ZEPOSIA and perform an appropriate diagnostic evaluation. If confirmed, treatment with ZEPOSIA should be discontinued.
Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) has been reported in MS patients treated with S1P receptor modulators who developed PML and subsequently discontinued treatment. IRIS presents as a clinical decline in the patient’s condition that may be rapid, can lead to serious neurological complications or death, and is often associated with characteristic changes on MRI. The time to onset of IRIS in patients with PML was generally within a few months after S1P receptor modulator discontinuation. Monitoring for development of IRIS and appropriate treatment of the associated inflammation should be undertaken.
Bradyarrhythmia and Atrioventricular Conduction Delays: Since initiation of ZEPOSIA may result in a transient decrease in heart rate and atrioventricular conduction delays, dose titration is recommended to help reduce cardiac effects. If treatment with ZEPOSIA is considered, advice from a cardiologist should be sought for those individuals:
- with significant QT prolongation
- with arrhythmias requiring treatment with Class 1a or III anti-arrhythmic drugs
- with ischemic heart disease, heart failure, history of cardiac arrest or myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disease, and uncontrolled hypertension
- with a history of Mobitz type II second-degree or higher AV block, sick sinus syndrome, or sino-atrial heart block
Liver Injury: Clinically significant liver injury, including acute liver failure requiring transplant, has occurred in patients treated with ZEPOSIA in the postmarketing setting. Signs of liver injury, including elevated serum hepatic enzymes and elevated total bilirubin, have occurred as early as ten days after the first dose. Obtain transaminase and bilirubin levels, if not recently available (i.e., within 6 months), before initiation of ZEPOSIA. Obtain transaminase levels and total bilirubin levels periodically during treatment and until two months after ZEPOSIA discontinuation. Patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of any hepatic injury. Patients who develop symptoms suggestive of hepatic dysfunction should have hepatic enzymes promptly checked, and ZEPOSIA should be interrupted. Treatment should not be resumed if a plausible alternative etiology for the signs and symptoms cannot be established, because these patients are at risk for severe drug-induced liver injury.
Fetal Risk: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Based on animal studies, ZEPOSIA may cause fetal harm. Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception to avoid pregnancy during treatment and for 3 months after stopping ZEPOSIA. Women who become pregnant while taking ZEPOSIA for MS may enroll in the ZEPOSIA pregnancy registry by calling 1-877-301-9314 or visiting
www.zeposiapregnancyregistry.com.
Increased Blood Pressure: Increase in systolic pressure was observed after about 3 months of treatment and persisted throughout treatment. Blood pressure should be monitored during treatment and managed appropriately.
Respiratory Effects: ZEPOSIA may cause a decline in pulmonary function. Spirometric evaluation of respiratory function should be performed during therapy, if clinically indicated.
Macular Edema: S1P modulators have been associated with an increased risk of macular edema. Obtain a baseline evaluation of the fundus, including a macula, near the start of treatment with ZEPOSIA. Perform an examination of the fundus, including the macula, periodically while on therapy and any time there is a change in vision. Continuation of ZEPOSIA therapy in patients with macular edema has not been evaluated. Macular edema over an extended period of time (i.e. 6 months) can lead to permanent visual loss. Consider discontinuing ZEPOSIA if macular edema develops. The risk of recurrence after rechallenge has not been evaluated.
Patients with a history of uveitis and patients with a history of diabetes mellitus are at increased risk of macular edema during ZEPOSIA therapy.
Cutaneous Malignancies: The risk of cutaneous malignancies (including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma) is increased in patients treated with S1P receptor modulators. Skin examinations are recommended prior to or shortly after the start of treatment and periodically thereafter for all patients, particularly those with risk factors for skin cancer. Providers and patients are advised to monitor for suspicious skin lesions. If a suspicious skin lesion is observed, it should be promptly evaluated. As usual for patients with increased risk for skin cancer, exposure to sunlight and ultraviolet light should be limited by wearing protective clothing and using sunscreen with a high protection factor. Concomitant phototherapy with UV-B radiation or PUV-A photochemotherapy is not recommended in patients taking ZEPOSIA.
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES): Rare cases of PRES have been reported in patients receiving a S1P receptor modulator. If a ZEPOSIA-treated patient develops unexpected neurological or psychiatric symptoms or any symptom/sign suggestive of an increase in intracranial pressure, a complete physical and neurological examination should be conducted. Symptoms of PRES are usually reversible but may evolve into ischemic stroke or cerebral hemorrhage. Delay in diagnosis and treatment may lead to permanent neurological sequelae. If PRES is suspected, treatment with ZEPOSIA should be discontinued.
Unintended Additive Immunosuppressive Effects From Prior Immunosuppressive or Immune-Modulating Drugs: When switching from drugs with prolonged immune effects, the half-life and mode of action of these drugs must be considered to avoid unintended additive immunosuppressive effects while at the same time minimizing risk of disease reactivation.
Severe Increase in Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Disability After Stopping ZEPOSIA: In MS, severe exacerbation of disease, including disease rebound, has been rarely reported after discontinuation of a S1P receptor modulator. The possibility of severe exacerbation of disease should be considered after stopping ZEPOSIA treatment so patients should be monitored upon discontinuation. After stopping ZEPOSIA in the setting of PML, monitor for development of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (PML-IRIS).
Immune System Effects After Stopping ZEPOSIA: After discontinuing ZEPOSIA, the median time for lymphocyte counts to return to the normal range was 30 days, with approximately 80% to 90% of patients in the normal range within 3 months. Use of immunosuppressants within this period may lead to an additive effect on the immune system, therefore caution should be applied when initiating other drugs 4 weeks after the last dose of ZEPOSIA.
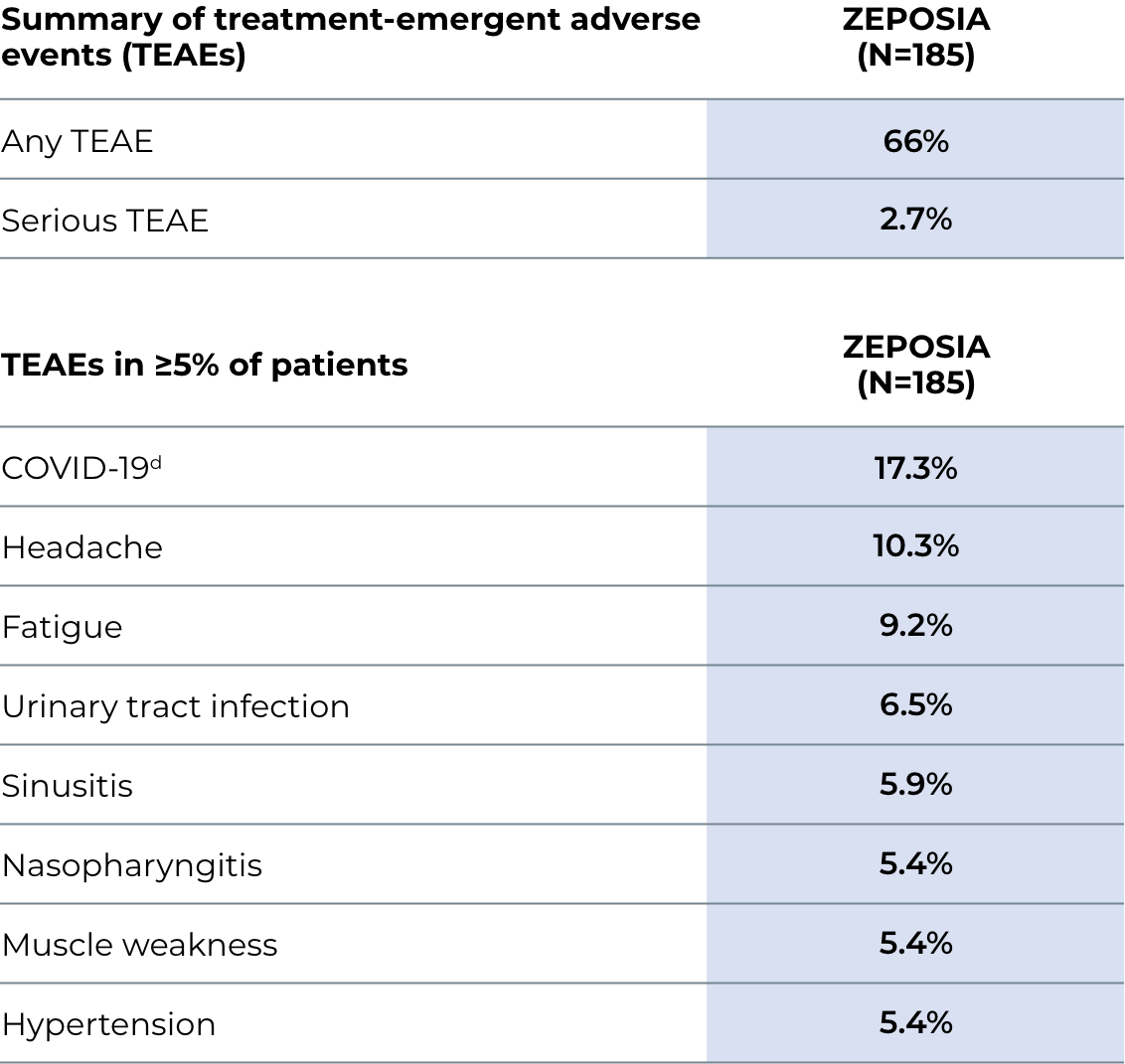
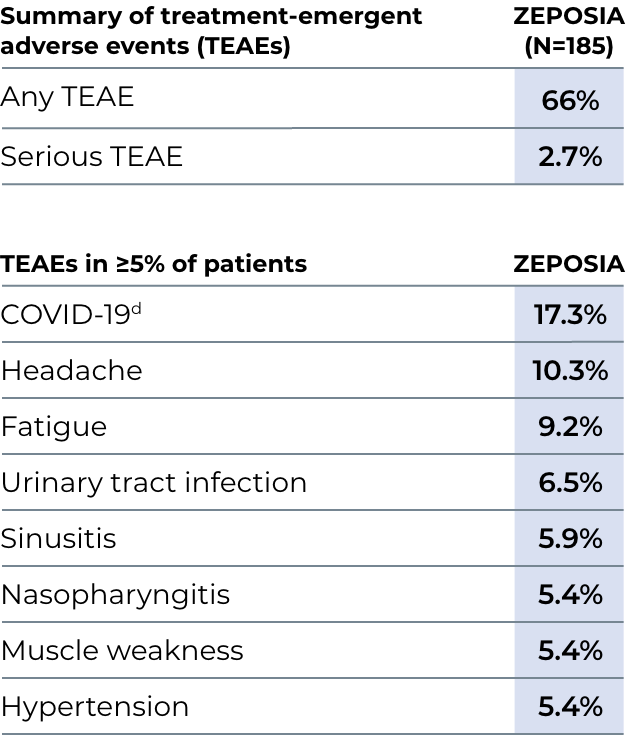
Most Common Adverse Reactions that occurred in the MS clinical trials of ZEPOSIA-treated patients (≥4%): upper respiratory infection, hepatic transaminase elevation, orthostatic hypotension, urinary tract infection, back pain, and hypertension.
In the UC clinical trials, the most common adverse reactions that occurred in ≥4% of ZEPOSIA-treated patients and greater than in patients who received placebo were upper respiratory infection, liver test increased, and headache.
Use in Specific Populations: Hepatic Impairment: Dosage adjustment in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A or B) is required, and use of ZEPOSIA in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) is not recommended.
For additional safety information, please see the full
Prescribing Information and
Medication Guide.
INDICATIONS
ZEPOSIA® (ozanimod) is indicated for the treatment of:
- Relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease, in adults.
- Moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) in adults.
References:
- Zeposia. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2024.
- Comi G, Kappos L, Selmaj KW, et al; SUNBEAM Study Investigators. Safety and efficacy of ozanimod versus interferon beta-1a in relapsing multiple sclerosis (SUNBEAM): a multicentre, randomised, minimum 12-month, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(11):1009-1020 and Suppl 1-26.
- Cohen JA, Comi G, Selmaj KW, et al; RADIANCE Trial Investigators. Safety and efficacy of ozanimod versus interferon beta-1a in relapsing multiple sclerosis (RADIANCE): a multicentre, randomised, 24-month, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(11):1021-1033 and Suppl 1-31.
- Selmaj KW, Steinman L, Comi G, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of ozanimod in relapsing multiple sclerosis: final analysis of the DAYBREAK open-label extension study. Poster presented at: ACTRIMS 2024 Forum; February 29–March 2, 2024; West Palm Beach, FL. Poster P090.
2084-US-2500094 04/25