
Well-Established
Safety Profile1,2a


Overall ZEPOSIA exposure in parent and extension trials (phase 1-3 MS, phase 2-3 UC) was 17,896.33 patient years (PY) and estimated to be 40,511 PY in the post-marketing setting. The cumulative number of patients exposed to ozanimod in parent and extension trials (all indications) was 4042 and estimated to be 51,736 in the post-marketing setting. Clinical trial data is current as of May 19, 2024, and post-marketing estimated data is current as of May 14, 2024.12,13
ZEPOSIA has been studied across multiple indications in 4 clinical trials, including TRUE NORTH (Ph 3); TOUCHSTONE (Ph 2); and SUNBEAM (Ph 3) and RADIANCE (Ph 3). 496 patients receiving the 0.92 mg orally once daily dose of ZEPOSIA during induction in TRUE NORTH or TOUCHSTONE and 882 patients receiving the 0.92 mg orally once daily dose of ZEPOSIA in SUNBEAM or RADIANCE were assessed in the safety analysis.1-4,6
In UC, from the start of the TOUCHSTONE phase 2 clinical trial (December 26, 2012) through TRUE NORTH OLE study data cutoff (June 30, 2023). In MS, from the start of the RADIANCE phase 2 clinical trial (September 18, 2012) through the DAYBREAK OLE database lock (April 7, 2023). Only includes patients receiving the 0.92 mg oral daily dose of ZEPOSIA.1,2,5,14,15
From the first patient randomized (October 18, 2012) through the DAYBREAK database lock (April 7, 2023), the maximum continuous exposure was 117.2 months. The mean exposure to ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg in the parent trials and DAYBREAK was 74.8 months.15
Moderate-to-severe UC: TRUE NORTH (NCT02435992), a phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial; TRUE NORTH OLE (NCT02531126), an ongoing phase 3, multicenter, OLE trial; TOUCHSTONE (NCT01647516), a phase 2, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial; JAPAN TRUE NORTH (NCT03915769), a phase 2/3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, treat-through study.
2,6-8,10
Relapsing MS: SUNBEAM (NCT02294058) and RADIANCE (NCT02047734), 2 phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active treatment-controlled studies; DAYBREAK (NCT02576717), a phase 3, multicenter, OLE trial; ENLIGHTEN (NCT04140305), an ongoing phase 3b, multicenter, longitudinal, open-label, single arm study.1,3,4,9,11,15
Safety Comparable to Avonex in Overall Incidence of AEs, and Generally Similar Safety in Long-Term Extension Study;
10 Years* of Experience1,15-17
| SUNBEAM (1 YEAR) | RADIANCE (2 YEARS) | ||||||
| Summary of Adverse Reactions | Avonex n=445 | ZEPOSIA n=448 | Avonex n=440 | ZEPOSIA n=434 | |||
| Overall incidence of adverse reactions | 75.5% | 59.8% | 83.0% | 74.7% | |||
| Severe adverse reactions | 2.2% | 1.6% | 4.3% | 3.5% | |||
| Serious adverse reactions | 2.5% | 2.9% | 6.4% | 6.5% | |||
| SUNBEAM (1 YEAR) | |||
| Summary of Adverse Reactions | Avonex n=445 | ZEPOSIA n=448 | |
| Overall incidence of adverse reactions | 75.5% | 59.8% | |
| Severe adverse reactions | 2.2% | 1.6% | |
| Serious adverse reactions | 2.5% | 2.9% | |
| RADIANCE (2 YEARS) | |||
| Summary of Adverse Reactions | Avonex n=440 | ZEPOSIA n=434 | |
| Overall incidence of adverse reactions | 83.0% | 74.7% | |
| Severe adverse reactions | 4.3% | 3.5% | |
| Serious adverse reactions | 6.4% | 6.5% | |
Adverse Reactions With an Incidence of at Least 2% in Patients Treated With ZEPOSIA and at Least 1% Greater Than Avonex1,16,17a
SUNBEAM AND RADIANCE: POOLED DATA
| Adverse Reactions | Avonex n=885 | ZEPOSIA n=882 | |
| Upper respiratory infectionb | 23% | 26% | |
| Hepatic transaminase elevationc | 5% | 10% | |
| Orthostatic hypotension | 3% | 4% | |
| Urinary tract infection | 3% | 4% | |
| Back pain | 3% | 4% | |
| Hypertensiond | 2% | 4% | |
| Upper abdominal pain | 1% | 2% |
Adverse reactions are sorted by decreasing incidence in patients treated with ZEPOSIA. For adverse reactions pertaining to liver function tests, increases were transient and generally resolved without discontinuation.
Elevations of 3-fold the ULN or greater occurred in 5.5% of patients taking ZEPOSIA and in 3.1% of patients taking Avonex. The majority (79%) continued treatment with ZEPOSIA with values returning to less than 3 times the ULN within approximately 2 to 4 weeks.1,16
From the first patient randomized (October 18, 2012) through the DAYBREAK database lock (April 7, 2023), the maximum continuous exposure was 117.2 months. The mean exposure to ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg oral daily dose in the parent trials and DAYBREAK was 74.8 months.1,15
Data are not an adequate basis for comparison of rates between ZEPOSIA and the active control.1
Includes the following terms: nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, rhinitis, respiratory tract infection viral, viral upper respiratory tract infection, rhinorrhea, tracheitis, and laryngitis.1
Includes the following terms: alanine aminotransferase increased, gamma-glutamyl transferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, hepatic enzyme increased, liver function test abnormal, and transaminases increased.1
Includes hypertension, essential hypertension, and orthostatic hypertension.1
DAYBREAK OLE: Incidence of Adverse Events15
| Summary of TEAEs (PRIMARY ENDPOINT) | ZEPOSIA (n=2494) | IR/1000 PY | |
| Any TEAE | 89.0% | 650.8 | |
| Severe TEAEs | 9.6% | 19.8 | |
| Serious TEAEs | 15.3% | 32.4 | |
| TEAEs leading to permanent treatment discontinuation | 3.9% | 7.7 |
TEAEs in ≥5% of Patients Treated With ZEPOSIA15
| TEAEs | ZEPOSIA (N=2494) | IR/1000 PY | |
| Nasopharyngitis | 21.3% | 49.6 | |
| Headache | 17.1% | 38.3 | |
| COVID-19 | 16.5% | 33.5 | |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 12.4% | 26.7 | |
| Lymphopeniae | 10.3% | 22.2 | |
| Back pain | 9.6% | 20.1 | |
| ALC decreasede | 9.4% | 20.0 | |
| Hypertensionf | 9.2% | 19.3 | |
| GGT increased | 8.0% | 16.7 | |
| Urinary tract infection | 6.8% | 13.9 | |
| Respiratory tract infection | 6.6% | 13.6 | |
| Arthralgia | 6.5% | 13.3 | |
| Bronchitis | 6.3% | 12.9 | |
| Depression-related TEAEsg | 5.9% | 12.0 | |
| Viral respiratory tract infection | 5.8% | 11.9 | |
| ALT increased | 5.1% | 10.2 |
Similar safety patterns were seen in the continuous once-daily oral ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg (n=881) population1,15
ALC reductions are an expected pharmacodynamic effect related to the mechanism of ozanimod; although investigators were not required to report ALC reductions as TEAEs, lymphopenia and ALC decreases were reported as TEAEs according to investigator determination.15
Includes preferred terms of hypertension, essential hypertension, labile hypertension, and systolic hypertension.15
Includes preferred terms of depression, depressed mood, and depressive symptoms.15
Demonstrated Tolerability Profile With Low Discontinuation Rates Due to Adverse Events1,15-17
≥90% of Patients Stayed on Therapy Through Completion
of Pivotal Trials
SUNBEAM (1 Year)
Remained on ZEPOSIA at 1 Year and 92% remained on Avonex1
RADIANCE (2 Years)
Remained on ZEPOSIA at 2 Years and 85% remained on Avonex1
LOW DISCONTINUATION RATES
DUE TO AEs15-17
SUNBEAM (1 Year)
For ZEPOSIA and 3.6% for Avonex16
RADIANCE (2 Years)
For ZEPOSIA and 4.1% for Avonex17
DAYBREAK (Up to 7 Years) n=2494
For ZEPOSIA in Long-Term Extension Study15
Rates of Serious Infections
and Malignancies Consistent
vs Avonex
The rate of serious infections at 1 year for ZEPOSIA was 1.1% vs 0.7% for Avonex, and the rate at 2 years for ZEPOSIA
was 0.9% vs 0.9% for Avonex. The rate of malignancies at 1 year for ZEPOSIA was 0.2% vs 0% for Avonex, and the rate at 2 years for ZEPOSIA was 0.9% vs 0.5% for Avonex.16,17
► Overall Infections
In SUNBEAM and RADIANCE, the overall rate of infections with ZEPOSIA (35%) was similar to Avonex (34%). ZEPOSIA causes a reduction in peripheral blood lymphocyte count and may increase the risk of infection.1
Controlled Lymphocyte Reductions
ALC was consistently maintained near the lower limit of normal across both pivotal trials, and the mean ALC for both SUNBEAM and RADIANCE was ≈0.8 × 109/L.16-18
VIEW ALC DATAHerpetic Infections
In active-controlled MS trials, herpes zoster was reported as an adverse reaction in 0.6% of patients treated with once-daily oral ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg and in 0.2% of patients taking Avonex.1
ZEPOSIA Consistently Maintained ALC Near the Lower Limit of Normal16-18
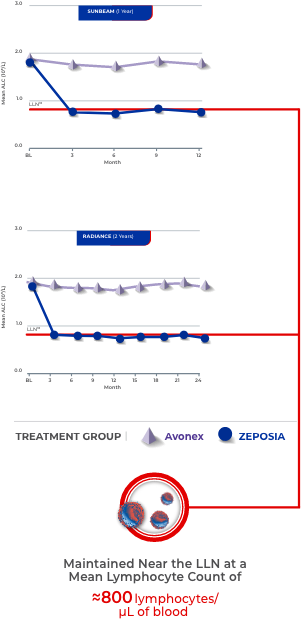
Lymphocyte numbers can be restored to normal values by discontinuing therapy1,16,17,19
- After discontinuing daily oral ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg, the median time for peripheral blood lymphocytes to return to the normal range was 30 days, with approximately 90% of patients in the normal range within 3 months
- Mean ALC was approximately 0.8 x 109 cells/L for both SUNBEAM and RADIANCE (at 1 year and 2 years, respectively)
- ZEPOSIA causes a mean reduction in peripheral blood lymphocyte count to approximately 45% of baseline values because of reversible sequestration of lymphocytes in lymphoid tissues; ZEPOSIA may therefore increase the susceptibility to infections, some serious in nature
BL=baseline; LLN=lower limit of normal.
Herpetic Infections
In active-controlled MS trials, herpes zoster was reported as an adverse reaction in 0.6% of patients treated with once-daily oral ZEPOSIA 0.92 mg and in 0.2% of patients taking Avonex.1
started on ZEPOSIA
Start Form
and help them get started on treatment.

This website is best viewed
using the horizontal display on
your tablet device.

This website is best viewed
using the vertical display on
your mobile device.


